Dodge Journey: Diagnosis and Testing
BRAKE ROTOR
Any servicing of the rotor requires extreme care to maintain the rotor within service tolerances to ensure proper brake action.
Excessive runout or wobble in a rotor can increase pedal travel due to piston knock-back. This increases guide pin sleeve wear due to the tendency of the caliper to follow the rotor wobble.
When diagnosing a brake noise or pulsation, the machined disc braking surface should be inspected.
BRAKING SURFACE INSPECTION
Light braking surface scoring and wear is acceptable. If heavy scoring or warping is evident, the rotor must be refaced or replaced. Excessive wear and scoring of the rotor can cause improper lining contact on the rotor's braking surface. If the ridges on the rotor are not removed before new brake shoes are installed, improper wear of the shoes will result.
If a vehicle has not been driven for a period of time, the rotor's braking surface will rust in the areas not covered by the brake shoes at that time. Once the vehicle is driven, noise and chatter from the disc brakes can result when the brakes are applied.
Some discoloration or wear of the rotor surface is normal and does not require resurfacing when linings are replaced. If cracks or burned spots are evident, the rotor must be replaced.
ROTOR MINIMUM THICKNESS
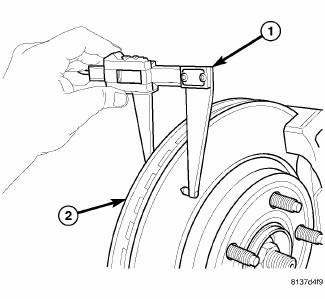
Fig. 153: MEASURING ROTOR THICKNESS
Measure rotor thickness (1) at the center of the brake pad contact surface. Replace the rotor if it is worn below minimum thickness or if machining the rotor will cause its thickness to fall below specifications.
CAUTION: Do not machine the rotor if it will cause the rotor to fall below minimum thickness.
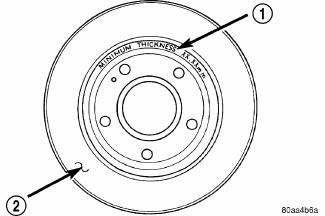
Fig. 154: Minimum
- - ROTOR MINIMUM THICKNESS MARKING
- - ROTOR
Minimum thickness specifications are cast on the rotor's unmachined surface (1).
ROTOR THICKNESS VARIATION
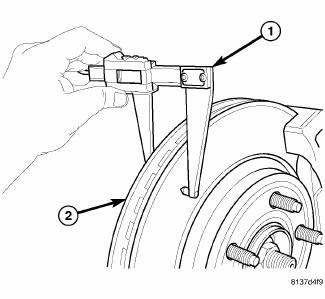
Fig. 155: MEASURING ROTOR THICKNESS
Thickness variation in a rotor's braking surface can result in pedal pulsation, chatter and surge. This can also be caused by excessive runout in the rotor or the hub.
Rotor thickness variation measurements should be made in conjunction with measuring runout. Measure thickness of the brake rotor (2) at 12 equal points around the rotor braking surface with a micrometer (1) at a radius approximately 25 mm (1 inch) from edge of rotor. If thickness measurements vary beyond the specification listed in the specification table.
ROTOR RUNOUT
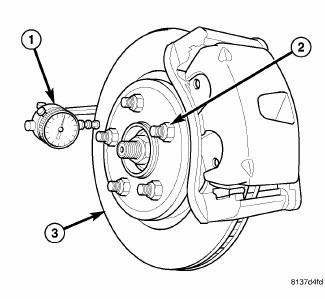
Fig. 156: MEASURING ROTOR RUNOUT
On-vehicle rotor runout is the combination of the individual runout of the hub face and the runout of the brake rotor (hub runout can be measured separately). To measure rotor runout on the vehicle:
1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
3. Install standard wheel mounting nuts, flat side to rotor, on all the wheel studs (2). Progressively tighten the nuts in a crisscross (star) pattern to 135 N.m (100 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Dial Indicator, Special Tool 9524, can be used in conjunction with C-3339A to measure in millimeters instead of inches. Dial indicator 9524 includes a finer scale to measure lower, tighter tolerances.
4. Mount Dial Indicator (1), Special Tool C-3339A, with Wheel, Special Tool 25w, or equivalent, to the knuckle. Position the dial indicator wheel to contact the rotor braking surface approximately 10 millimeters from the outer edge of the rotor (3).
5. Slowly rotate the brake rotor checking lateral runout, marking the low and high spots. Record these measurements.
6. Check and record the runout on the opposite side of the rotor in the same fashion, marking the low and high spots.
7. Compare runout measurement to specifications.
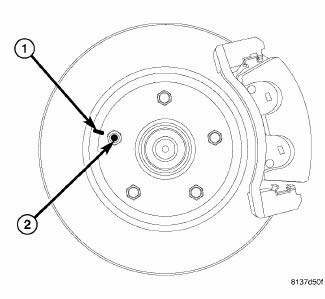
Fig. 157: WHEEL STUD AND ROTOR INDEX MARKED
If runout is in excess of specifications, check the lateral runout of the hub face. Before removing the rotor from the hub, place a chalk mark across both the rotor (1) and the one wheel stud (2) closest to where the high runout measurement was taken. This way, the original mounting spot of the rotor on the hub is indexed.
8. Remove the rotor from the hub.
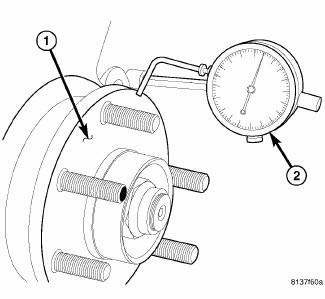
Fig. 158: MEASURING HUB RUNOUT
NOTE: Before measuring hub runout, clean the hub face surface with an appropriate cleaner. This provides a clean surface to get an accurate indicator reading.
NOTE: Dial Indicator, Special Tool 9524, can be used in conjunction with C-3339A to measure in millimeters instead of inches. Dial indicator 9524 includes a finer scale to measure lower, tighter tolerances.
9. Mount Dial Indicator (2), Special Tool C-3339A, to the knuckle. Position the dial indicator stem so it contacts the hub face (1) near the outer diameter. Care must be taken to position the stem outside of the stud circle, but inside of the chamfer on the hub rim.
10. Slowly rotate the hub measuring runout. Hub runout should not exceed 0.01 mm (0.0004 inch). If runout exceeds this specification, the hub must be replaced.
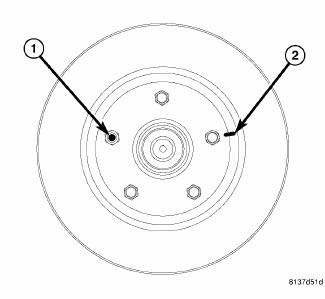
Fig. 159: ROTOR REINDEXED ON WHEEL STUDS
11. If hub runout does not exceed this specification, install the original rotor back on the hub, aligning the chalk mark on the rotor (2) with a wheel mounting stud, two studs apart from the original stud (1).
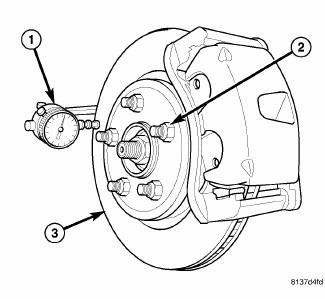
Fig. 160: MEASURING ROTOR RUNOUT
12. Install standard wheel mounting nuts, flat side to rotor, on all the wheel studs (2). Progressively tighten the nuts in a crisscross (star) pattern to 135 N.m (100 ft. lbs.).
13. Mount the Dial Indicator (1), Special Tool C-3339A, and remeasure runout on both sides of the brake rotor as explained in earlier steps to see if runout is now within specifications.
14. If runout is still not within specifications, reface or replace brake rotor.
 Rotor, brake
Rotor, brake
...
 Standard procedure
Standard procedure
BRAKE ROTOR MACHINING
NOTE: Refacing the rotor is not required each time the brake pads are
replaced, only
when the need is foreseen.
Any servicing of the rotor requires extreme care to ma ...
See also:
Installation
LEFT-HAND-DRIVE
NOTE: The master cylinder must be bled before installing it on the
vehicle.
1. Bench bleed the master cylinder.
2. Wipe the face of the power brake booster clean where the ...
POWER INVERTER — IF EQUIPPED
Your vehicle may be equipped with a 115 Volt AC (150
Watt maximum) power outlet located on the back of the
center console. This outlet can power cellular phones,
electronics and other low power dev ...
Case assembly, differential
DESCRIPTION
The differential gear system divides the torque between the axle shafts. It
allows the axle shafts to rotate at
different speeds when turning corners.
Each differential side gear is s ...
